0

0




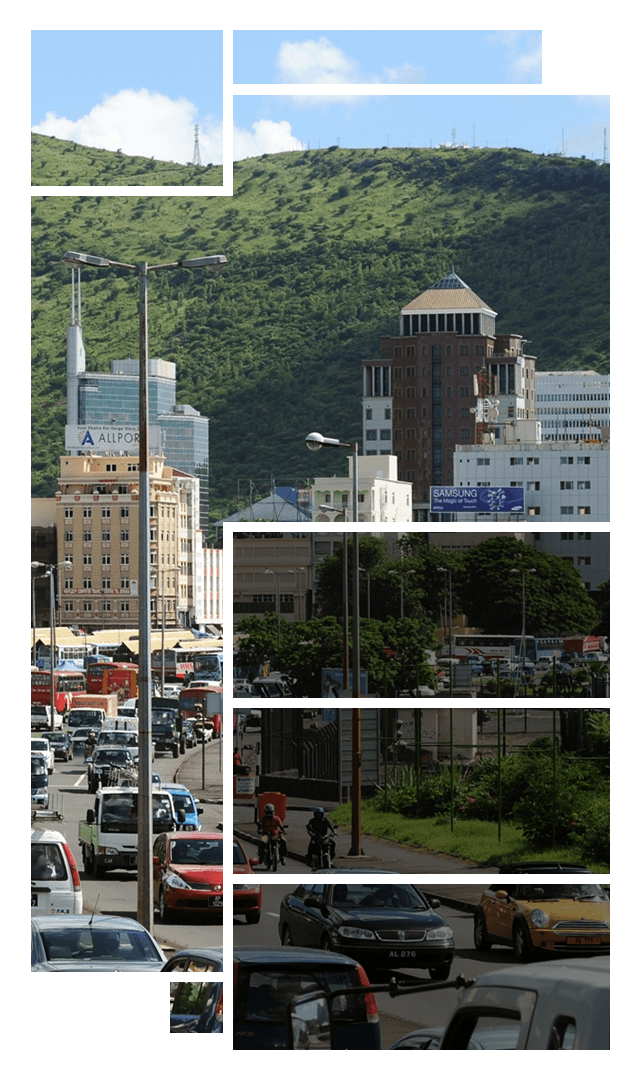
African cities’ planning and development is a priority to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and fight climate change.
Launched to contribute to this objective, CICLIA is the missing link between the implementation of international and national climate strategies and the concrete needs of these cities, which are facing an unprecedented rate of urbanization
CICLIA supports local African authorities in developing and financing low-carbon and resilient urban projects that serve the fight against climate change.
CICLIA’s commitment is essential to promote inclusive and sustainable projects that benefit the inhabitants of African cities.
Climate at the Heart of African cities' Development
CITIES AND CLIMATE IN AFRICA,
Funding and expertise for a sustainable development of African cities


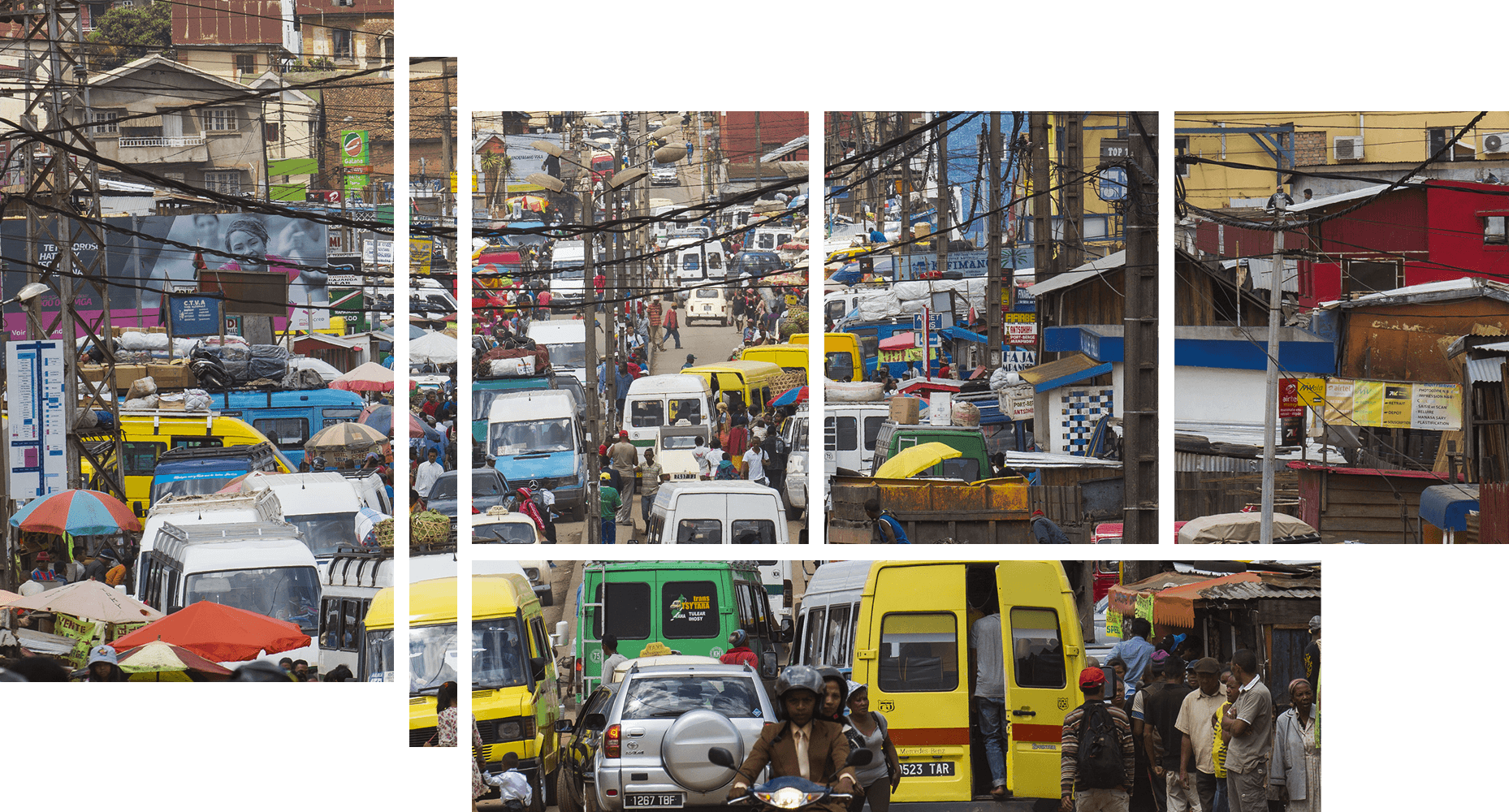
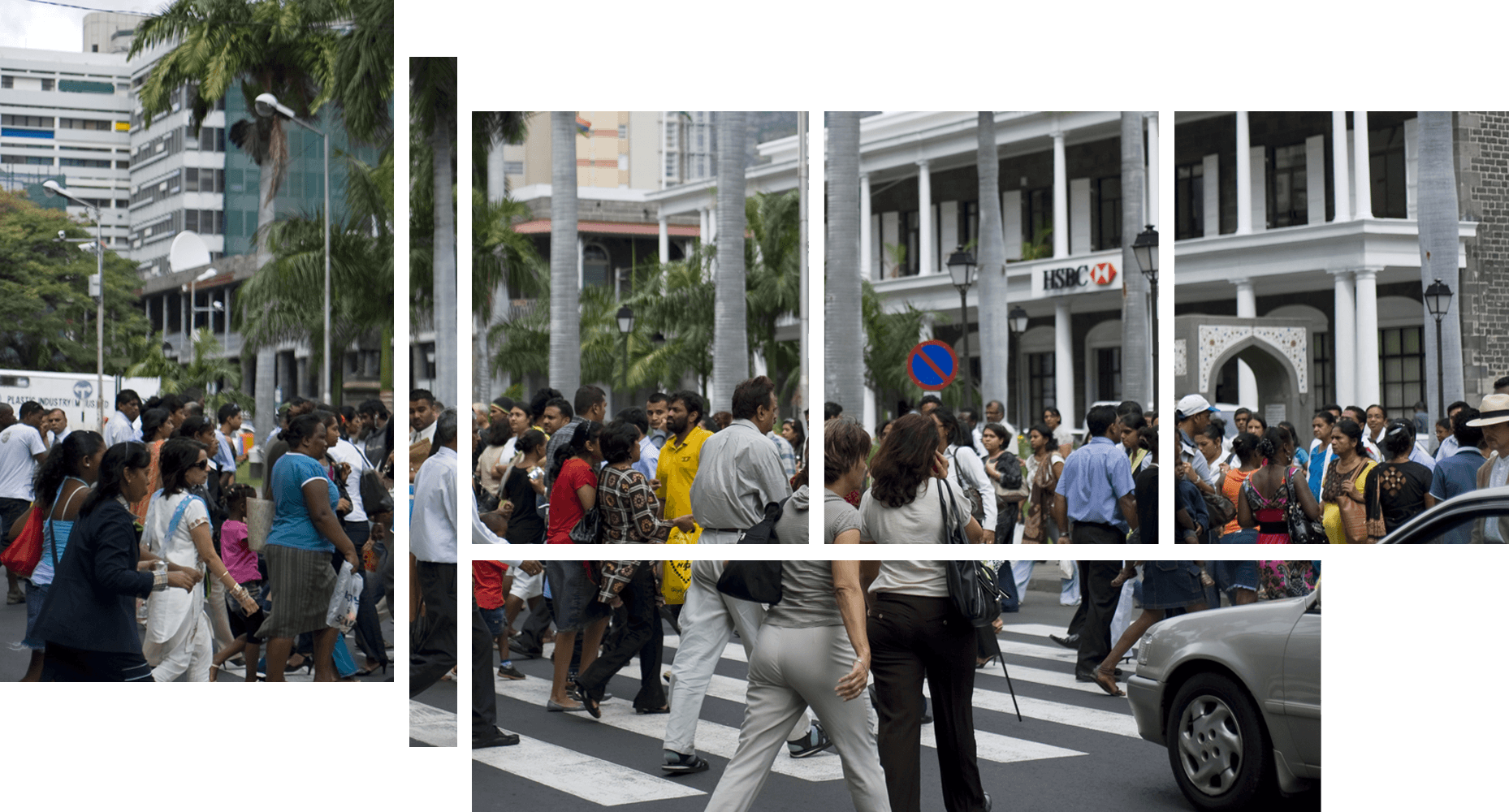
In Africa, there are more than 550 million city residents today
Increased exposure to climate change risks
The need for low-impact urban development









More than 550 million city residents in Africa today
Increased exposure to climate change risks
The need for
low-impact urban development
55%





More than 550 million city residents in Africa today
Increased exposure to climate change risks
The need for
low-impact urban development

Like everywhere else in the world, cities, which concentrate population and economic activities, significantly contribute to global warming.
They account for 70% of global energy-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. With low emissions at this stage, African cities can still have an impact on their growth and act in favor of low-carbon development.
70%





Strong demographic pressure and major rural transformations fuel the highest urban growth in the world (4% per year on average).


billion
001
2050
million
500
2022
nearly
1 billion
in 2050
More than 550 million city residents in Africa today
Increased exposure to climate change risks
The need for
low-impact urban development




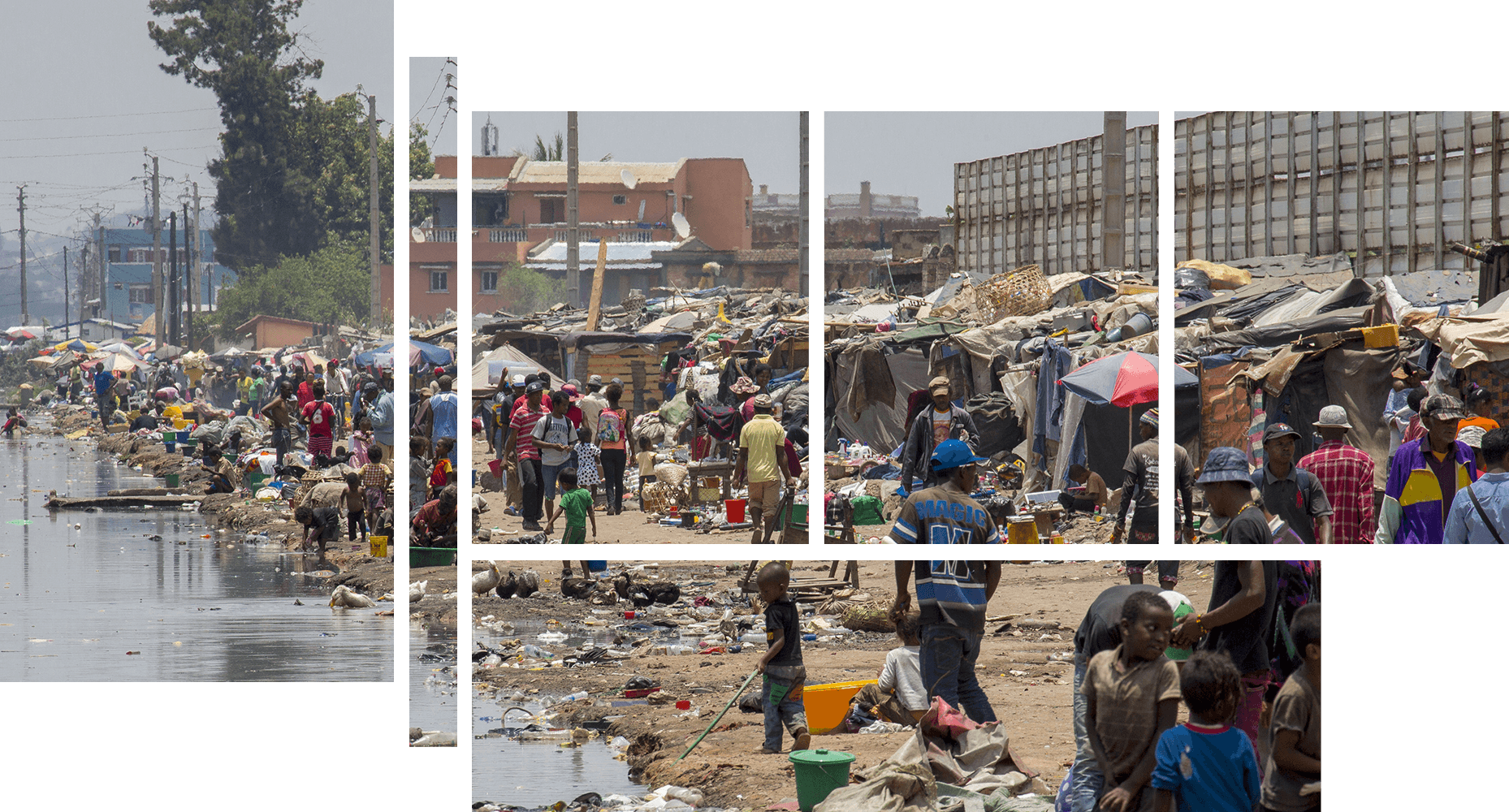
African cities are key stakeholders in planning and implementing the resilience of populations and infrastructures facing climate change, and in integrating their development into the objectives of sustainable development.
The majority of the required adaptation measures are or will be locally implemented. The local scale is relevant when facing challenges varying according to context, and it also allows the implementation of necessary mitigation and adaptation strategies.
As local public policy makers and service and infrastructure managers, cities are best positioned to implement national and international climate commitments while improving the daily lives of their populations.
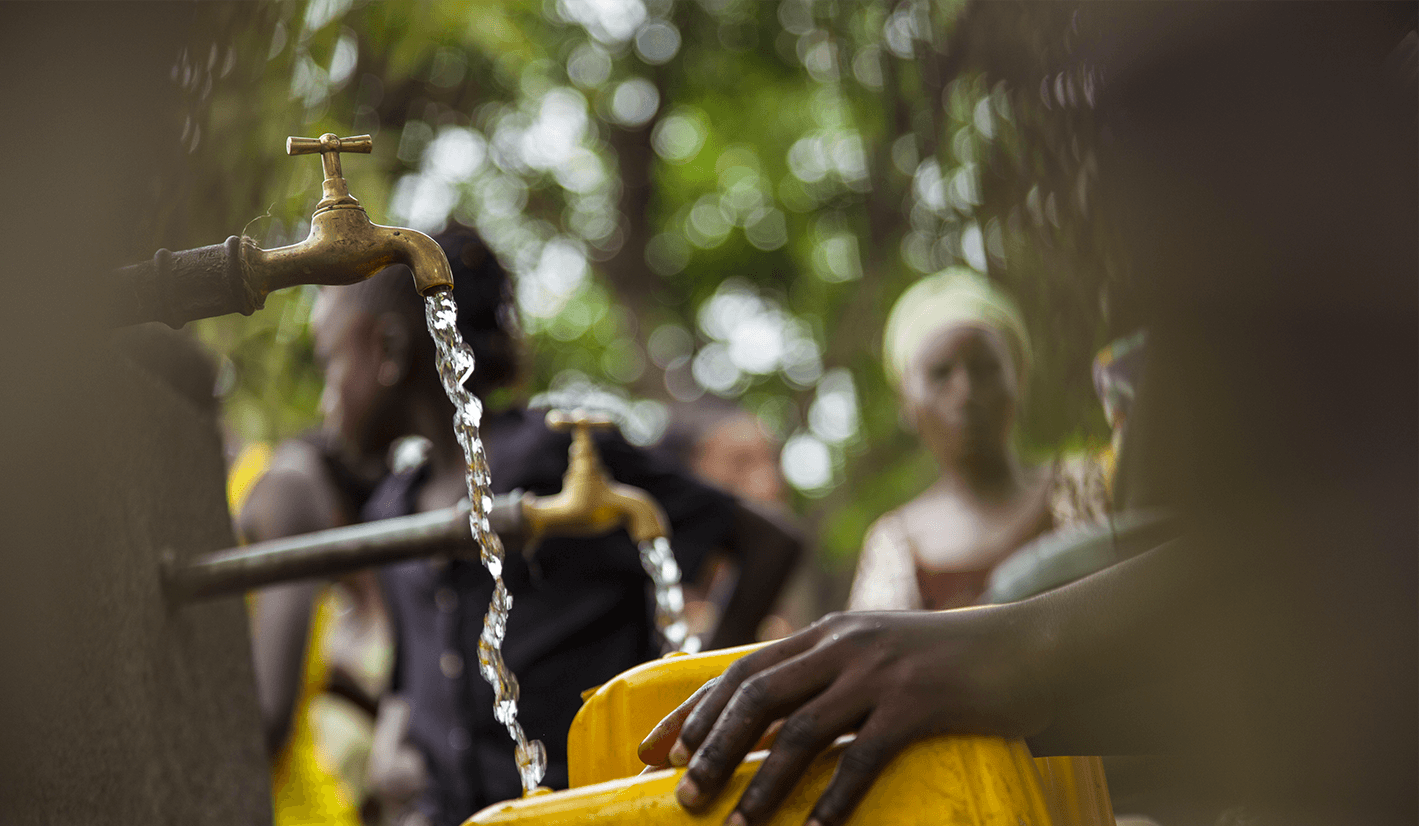

Today, the preservation of the planet as well as the strengthening of social cohesion and local institutions are the ambitions that drive CICLIA's action.
Imagining and implementing sustainable cities requires time for strategic and technical studies as well as for the mobilization of appropriate expertise.
CICLIA's support to cities before the investment has a threefold ambition:
CICLIA marks a turning point by placing climate change measures at the heart of urban development policies, strategies and programs.
Introduced in the wake of the Paris Agreements, CICLIA is one of the very first financing and support initiatives to integrate climate change issues into project preparation for African urban populations.



Focus on
Project classification



Focus on
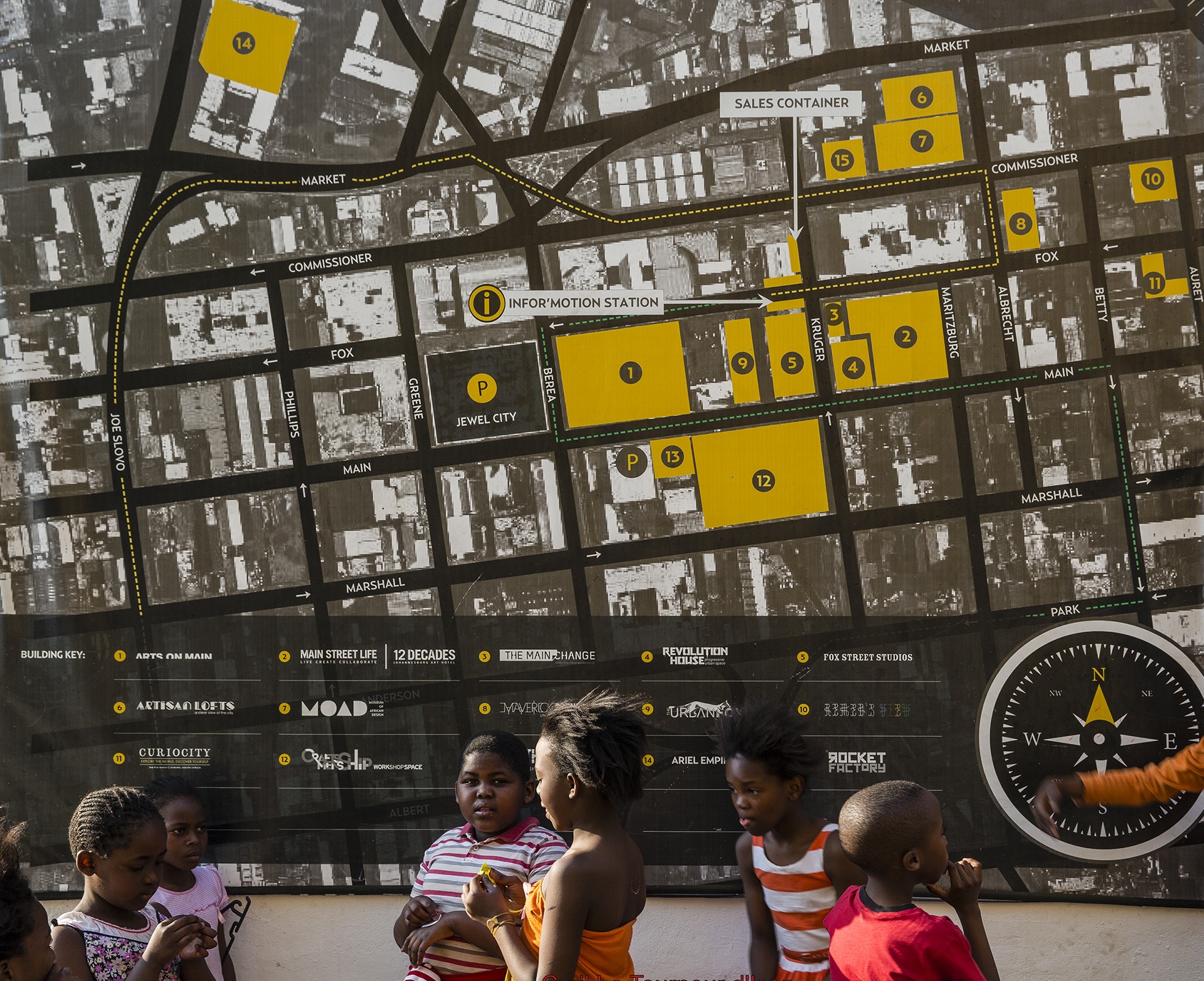
"Solar street lighting in Kampala: towards a more inclusive city"
Interview
with Olga Koukoui,
AFD Project Team Leader,
Urban Development,
Planning, Housing
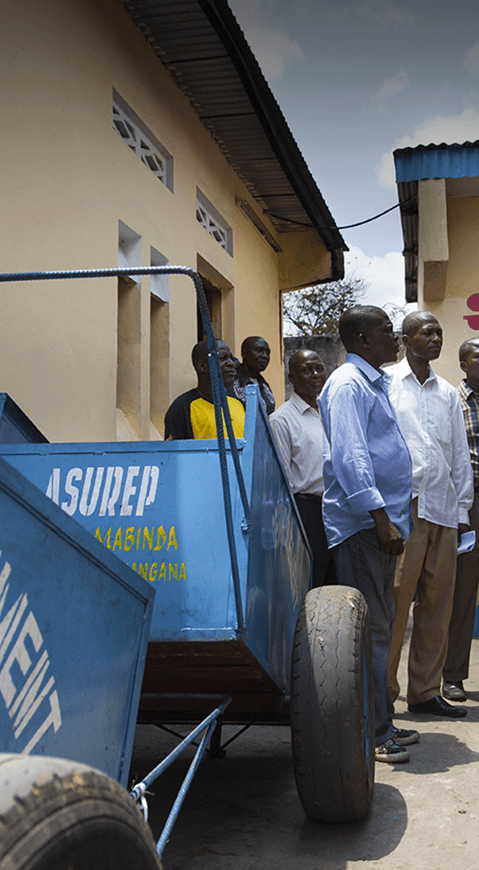






















Skills transfer
to local stakeholders
and support during
the study phase


2

Valorization, among African and international professionals, of the solutions provided by each project to the SDGs.



3

PREPARE
STRENGTHEN
LEARN




Developing local climate strategic frameworks and upstream studies on “sustainable city” investment projects

"A project starts with an idea, an identification, and then you have to prepare the project, otherwise you will never succeed…”
Robert Luzolanu,
Robert Luzolanu, Coordinator of the commune of Kinshasa’s urban development unit.


"We carry out capacity building actions for the community, including market facilities management and local taxation improvements."
Gabriel Charasse,
AFD Project Team Leader - Urban Development, Planning
and Housing Division

Study trip to Lomé: overview of an instructive peer-to-peer exchange of experience and best practice


2
of:
a financing

billion
euros
,
1,2
for the implementation of
11 infrastructure and urban services
projects
for the implementation of 11 infrastructure
and urban services projects
million
euros
510




preparation of
urban projects (infrastructure and service)
19


This technical assistance has already enabled:

technical
assistance
contracts
29
To this day, nearly
11 million euros
have been invested into


the Swiss Secretariat for Economic Affairs
million
euros
million
euros
European Union
8
3
from
co-donors
million
euros
11
which
enabled it
to raise



To finance its activities until april 2023, CICLIA received
To finance its activities
until april 2023,
CICLIA received a
€1,4 million
envelope from AFD
,
a
million euros envelope
from AFD


690
with 7 new projects
to be granted
in the next
2 years
million euros


11 projects :




39
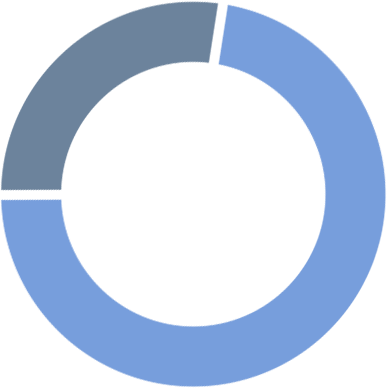
African cities












10 supportive of climate change mitigation,
3 mixed

Urban development (incl. precarious neighborhoods)

Solid waste

Energy

Transport & Mobility

Local economic development

Climate strategies and disaster risk management

Urban water











CICLIA's commitment is already producing significant outcomes.
Preservation of the planet, Improvement of social cohesion, Strengthening of local institutions,




tons of CO2 equivalent
can be avoided
.
-
-300.000

(including more than 3 million living under the poverty line) will see their living conditions improved thanks to access to basic services and green and sustainable infrastructure
million
of people
,
7,9
950
working in the cities supported by CICLIA have benefited from a strengthening of their capacity (knowledge, expertise, know-how)
people
more than


Monrovia (Liberia)




Bangui (CAR)


Kinshasa (DRC)



Ganvie
(Benin)


Uganda


Kenya


Conakry (Guinea)


Lomé
(Togo)


Kano (Nigeria)


Ogun (Nigeria)


Djibouti
(Djibouti)


Bobo-Dioulasso (Burkina Faso)


Mwanza (Tanzania)


Tanga (Tanzania)


Uganda


Kampala (Uganda)


Cape Town
(South Africa)


Durban
(South Africa)


Bobo-Dioulasso (Burkina Faso)


Cape Town
(South Africa)


Madagascar


Guinea


Abidjan
(Ivory Coast)


Yaounde
(Cameroon)
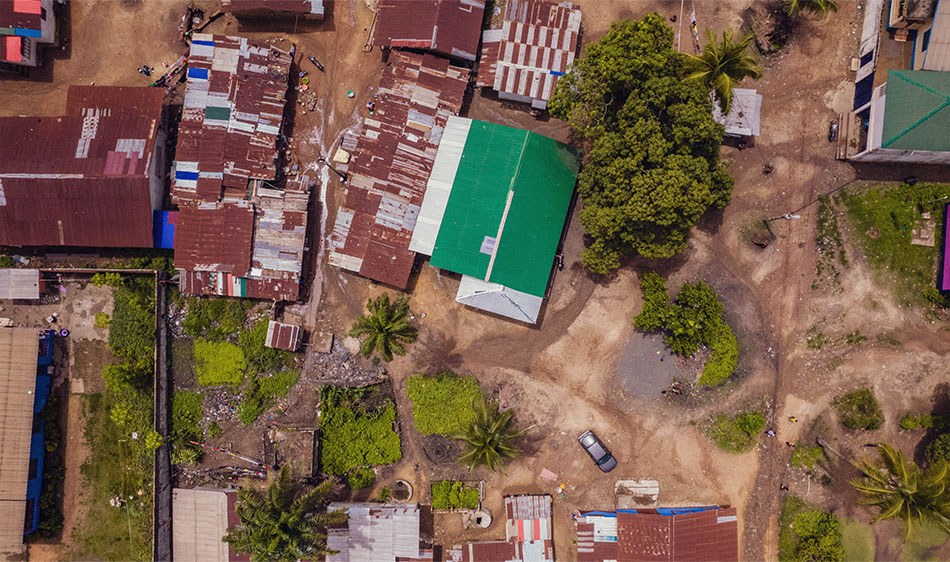








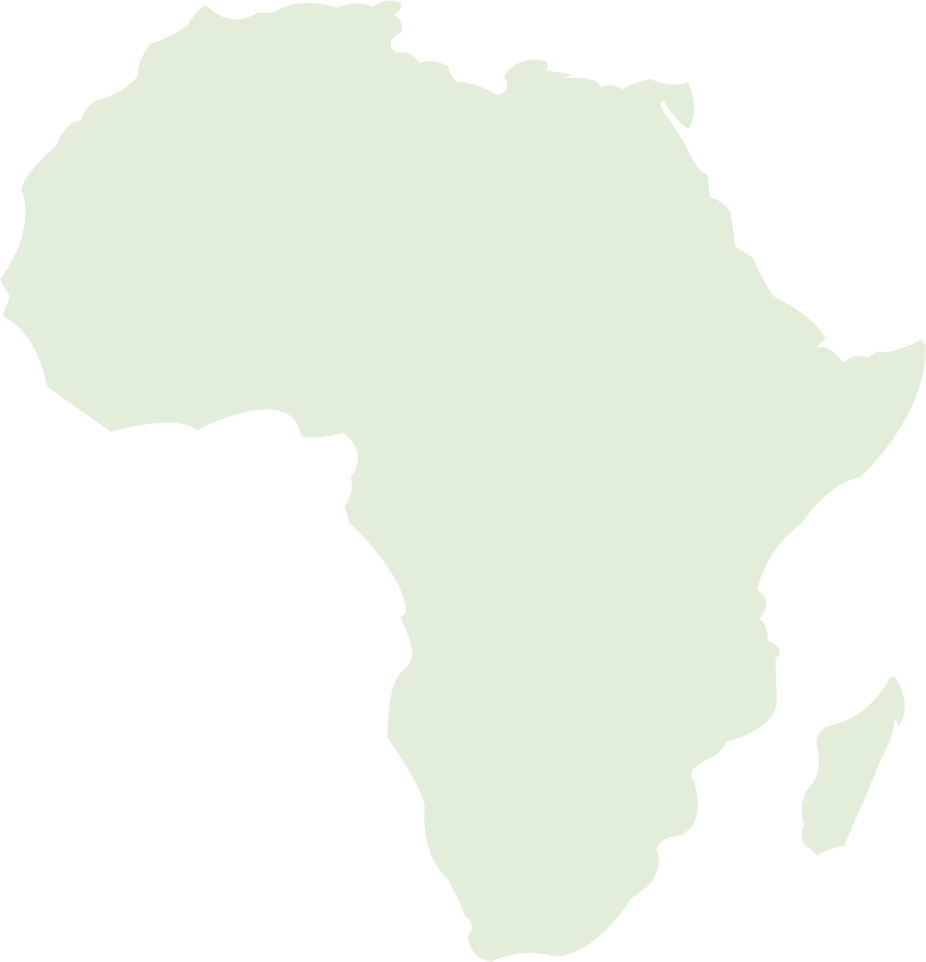


















MONROVIA Liberia
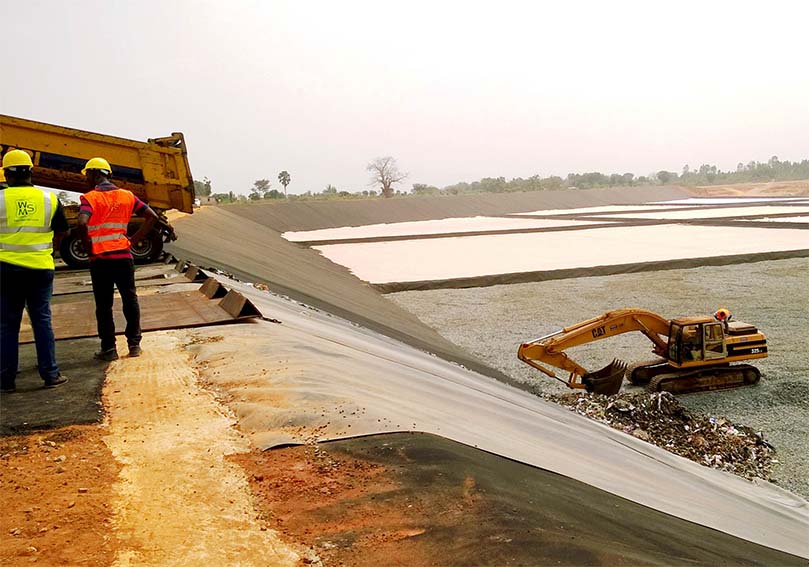



LOMÉ
Togo
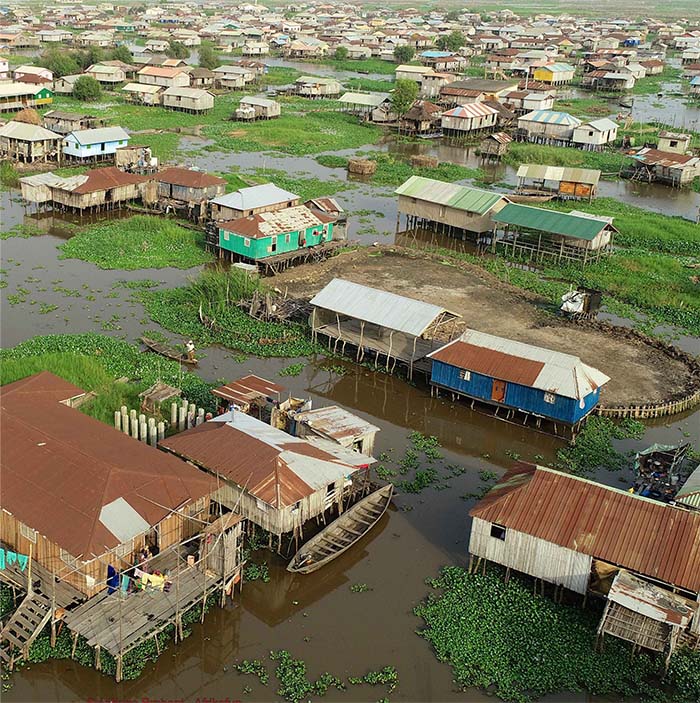




GANVIE
Benin
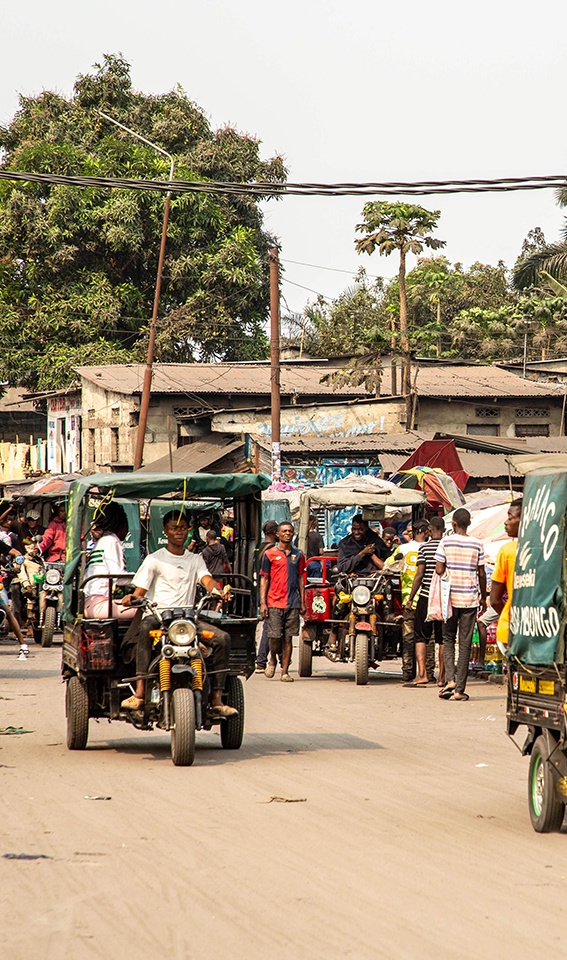
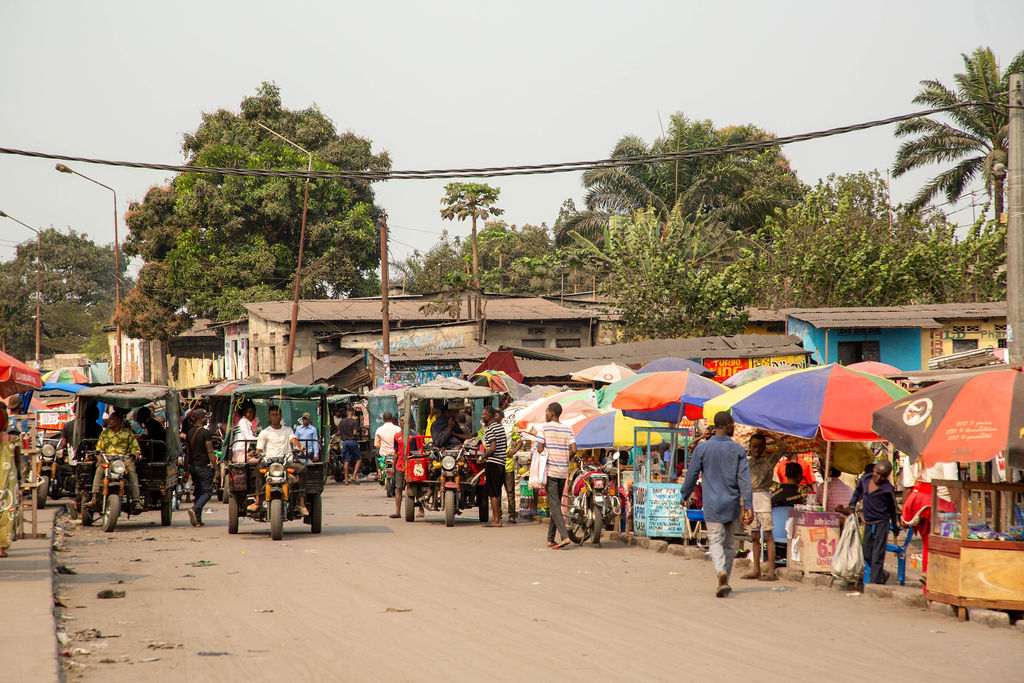




KINSHASA DRC
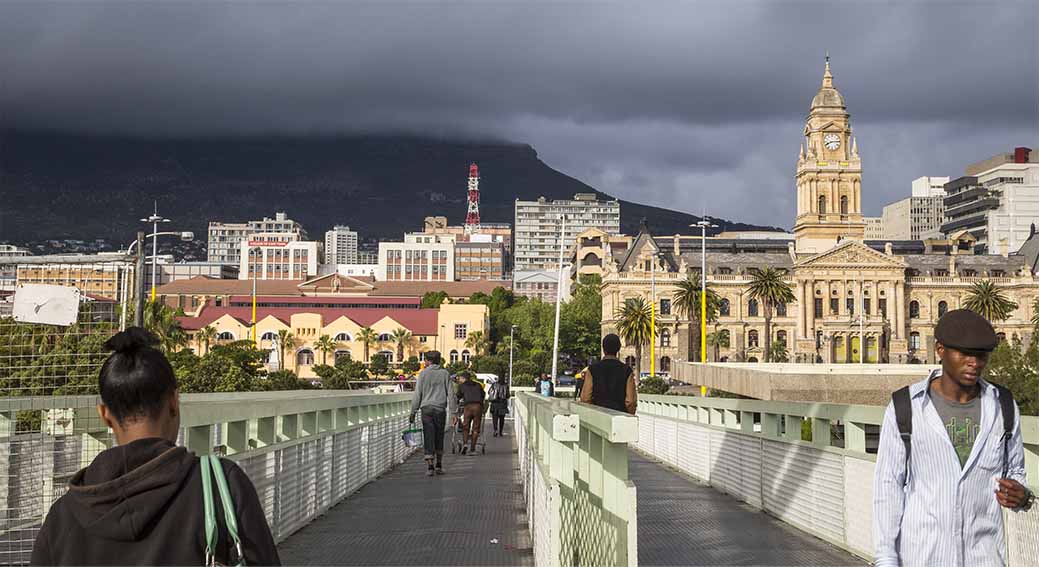
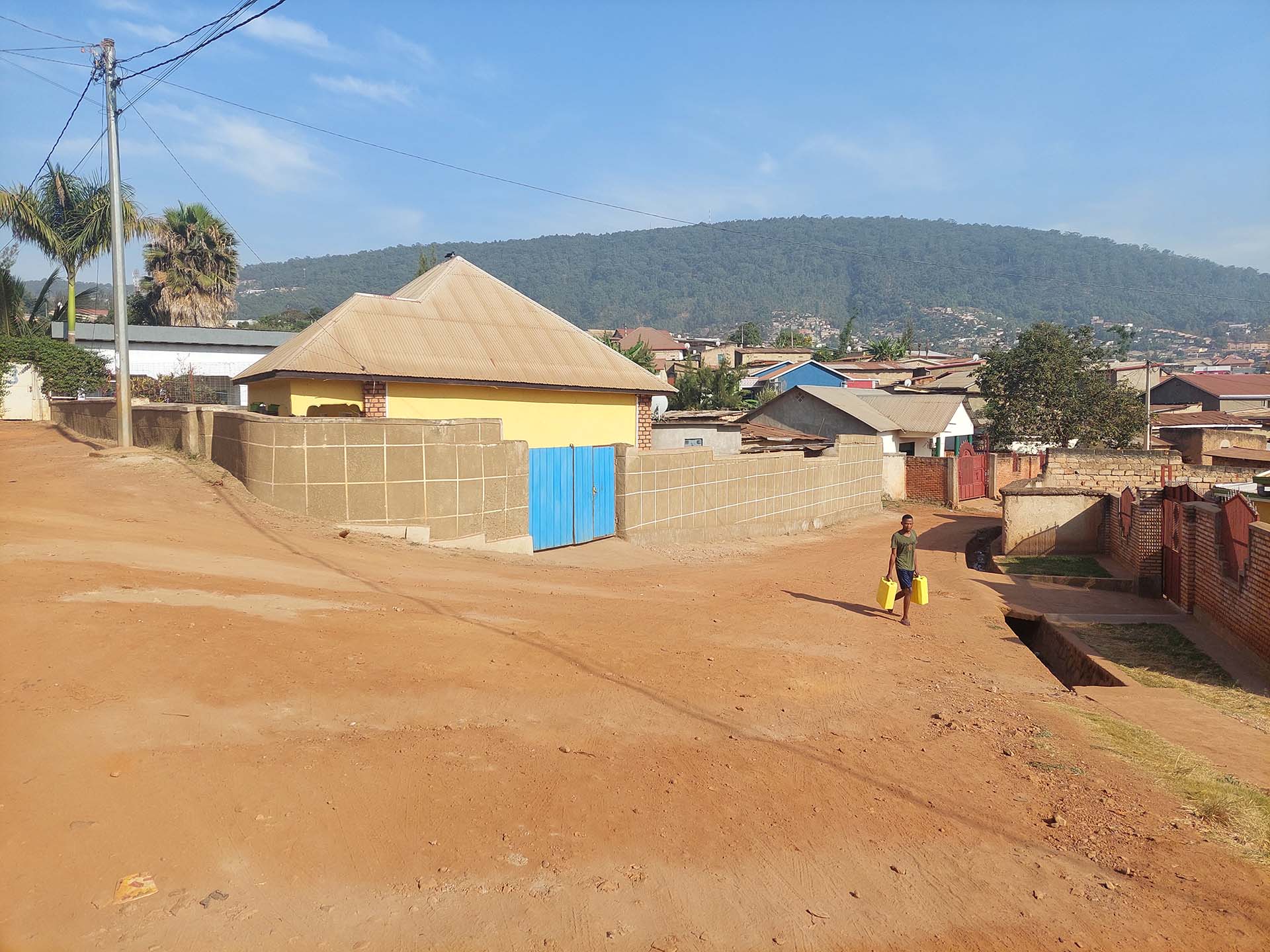
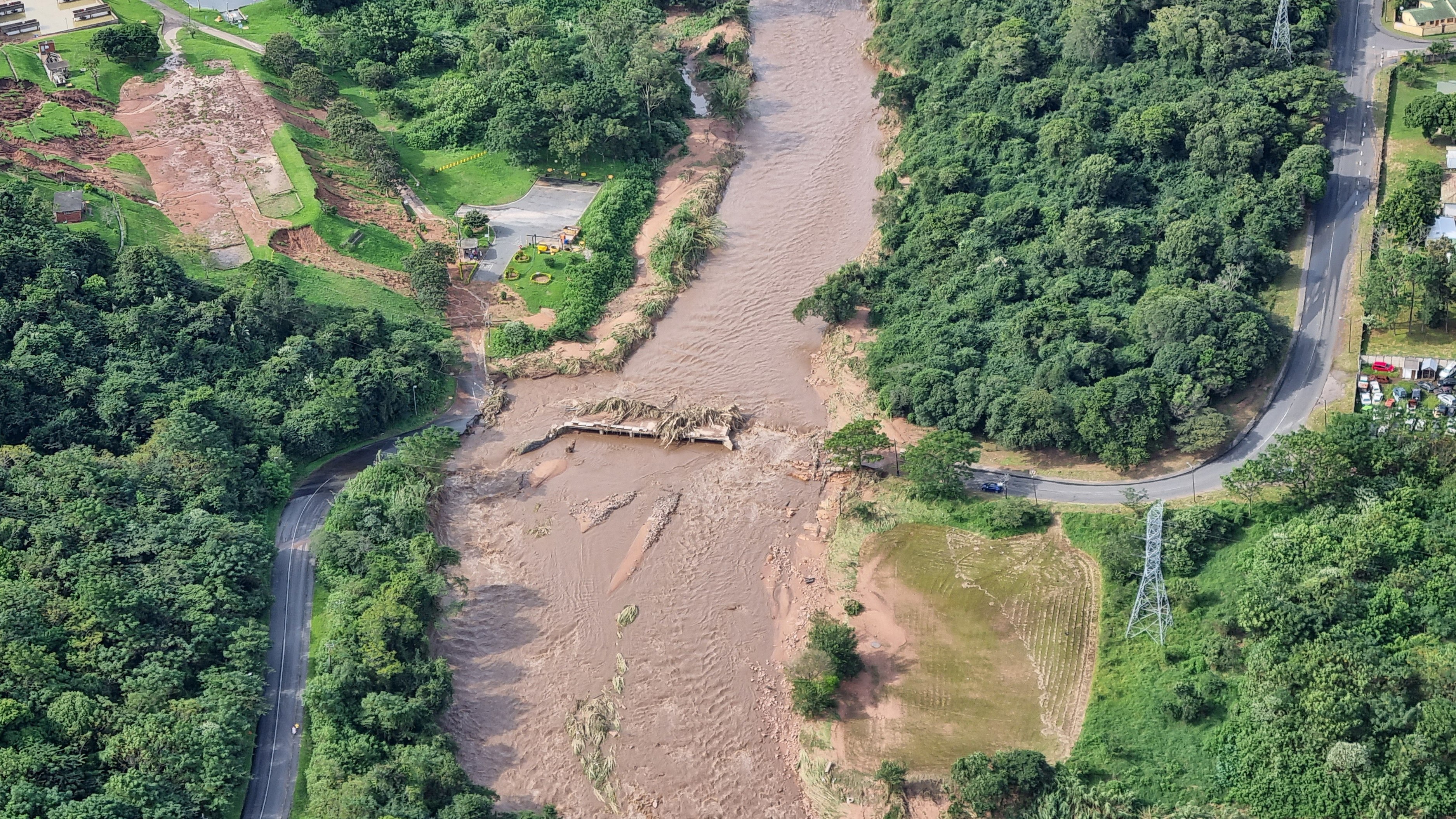











CAPE TOWN
South Africa
KIGALI
Rwanda
DURBAN
South Africa



Global Ambitions,
Local Implementation
Des ambitions globales,
des concrétisations locales
Global
Ambitions,
Local Implementations
Monrovia (Liberia)











Kigali (Rwanda)
Durban
(South Africa)
Kinshasa (DRC)
Ganvie
(Benin)
Lomé (Togo)
Lomé (Togo)
Cape Town
(South Africa)